There are many misconceptions in SEO regarding 404 errors and 301 redirects. Many believe that all 404 errors harm a website’s ranking and that a 301 redirect can be used universally when content is moved. Such misunderstandings can lead to ineffective strategies and significant traffic loss.
The purpose of this article is to explain what HTTP status codes 404 and 301 represent and to dispel common myths about their impact on SEO. It also provides practical recommendations on when and how to use each of these status codes to ensure proper site indexing and maintain high search visibility.
- What Is a 404 Error?
- Common Causes of 404 Errors
- Overview of the Google Indexing Process and How Page Deletion Triggers a 404 Error
- Do 404 Errors Affect SEO?
- Appropriate Use Cases for 404 Errors
- How a 404 Error Signals to Search Engines That a Page No Longer Exists and Stops Further Indexing Attempts
- Improper 404 Scenarios
- What Is a 301 Redirect?
- Analogy: Mail Forwarding
- How a 301 Redirect Informs Search Engines of a Page’s New Address
- How 301 Redirects Affect SEO
- Why You Should Not Use a 301 Redirect to the Homepage
- Problems of Semantic Relevance
- Possible Consequences of a 301 Redirect to the Homepage
- Best Practices for Managing 404 Errors and 301 Redirects
- Related Video
What Is a 404 Error?
A 404 error (“Not Found”) is one of the most common HTTP status codes on the internet. It indicates that the server successfully established a connection with the client’s browser but was unable to locate the requested page.
Common Causes of 404 Errors
I frequently encounter several common reasons for 404 errors:
-
Content relocation: When content is moved to a new URL without implementing a proper redirect.
-
Broken links: When internal or external links point to pages that no longer exist or have been moved.
-
Renamed URLs: When a page’s URL is changed but inbound links are not updated accordingly.
Overview of the Google Indexing Process and How Page Deletion Triggers a 404 Error
Google uses web crawlers (bots or spiders) to index pages. When a page is deleted, crawlers continue attempting to access it until they receive several 404 responses. These responses inform Google that the page no longer exists.
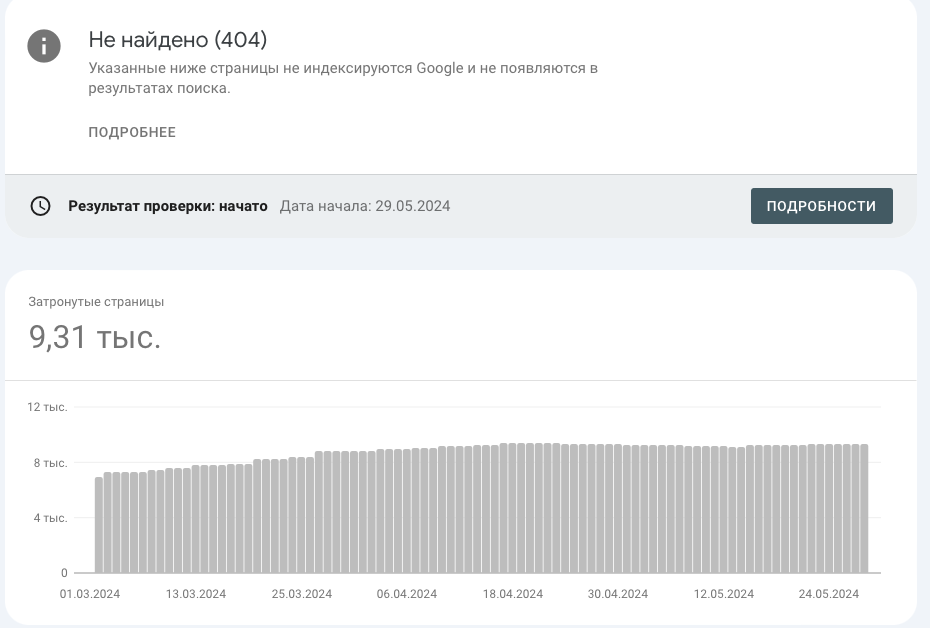
Until the page is deindexed, it may still appear in search results, but clicking on the link will return a 404 error. Over time, after receiving a sufficient number of 404 responses, Google removes the page from its index, preventing it from appearing in search results.
Thus, a 404 error serves as an important signal to search engines, helping them maintain the relevance and accuracy of their databases by removing non-existent pages.
Do 404 Errors Affect SEO?
When encountering 404 errors, it is crucial to analyze their cause. Depending on the context, their impact on SEO can vary. 404 errors can either be a normal part of content lifecycle management or a result of poor site maintenance.
Appropriate Use Cases for 404 Errors
There are scenarios where 404 errors are normal and even beneficial:
-
Product removal: When an item is discontinued and no replacement exists, the 404 status indicates the product is no longer available.
-
Outdated content: When obsolete or irrelevant content is deleted, returning a 404 response helps search engines understand that these pages should no longer be indexed.
How a 404 Error Signals to Search Engines That a Page No Longer Exists and Stops Further Indexing Attempts
When a page returns a 404 response, it informs search engines that the resource no longer exists, leading to:
- Index cleanup: Search engines stop attempting to crawl the page and remove it from their databases.
- Improved index quality: The index remains focused only on active, relevant pages.
Improper 404 Scenarios
However, some 404 errors result from mismanagement and can negatively affect SEO:
- Moved pages without redirects: If a page is relocated without a 301 redirect, both users and search engines encounter 404 errors, resulting in traffic loss and ranking decline.
To avoid this, proper redirect management is essential. By ensuring that all outdated URLs are redirected to their relevant new pages, you can preserve link equity and maintain SEO performance.
404 errors are not always harmful to SEO, but proper management of them is critically important. It is essential to distinguish between appropriate and inappropriate occurrences of these errors and act accordingly.
What Is a 301 Redirect?
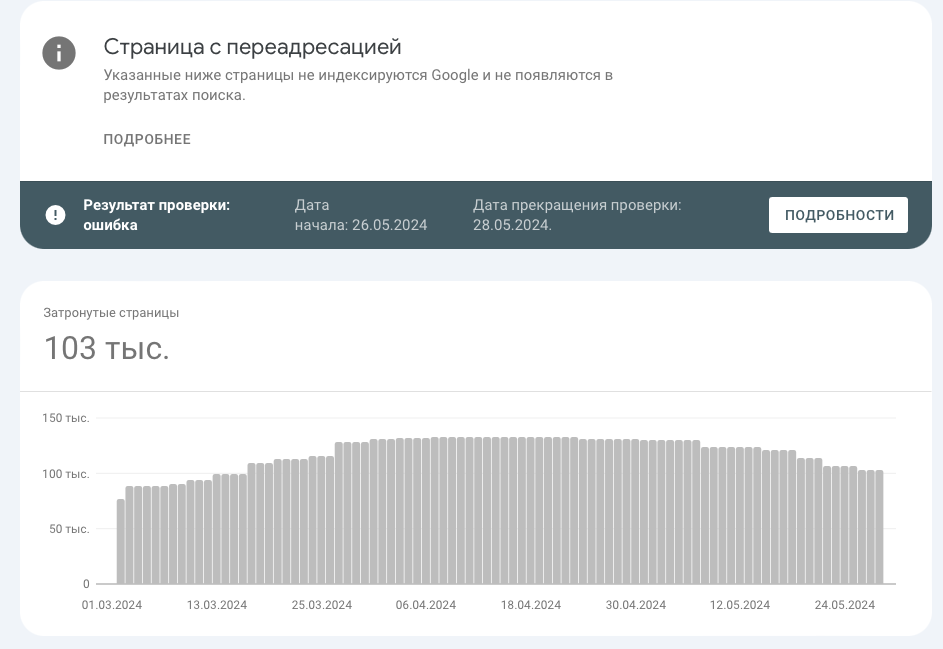
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another. It tells browsers and search engines that a page has permanently moved to a new address. It is the most reliable method to preserve traffic and SEO value when changing URLs.
Analogy: Mail Forwarding
Imagine that you’ve moved to a new address and filed a forwarding request with your local postal service. Each time someone sends mail to your old address, the postal service automatically forwards it to your new one. The same principle applies to a 301 redirect — whenever someone attempts to visit the old URL, they are automatically redirected to the new address.
How a 301 Redirect Informs Search Engines of a Page’s New Address
When a 301 redirect is configured, the server returns this status code whenever a request is made to the old URL. This signals to search engines that the content has been permanently moved to a new address, prompting them to update their indexes accordingly. Over time, search engines replace the old URL with the new one in their databases.
How 301 Redirects Affect SEO
One of the key advantages of using a 301 redirect is that it allows the transfer of most of the link equity (ranking power) from the old URL to the new one. When implemented correctly, a 301 redirect passes approximately 90–99% of the original link value. This ensures that the new page retains most of the SEO authority of the previous one, including search rankings, backlinks, and accumulated trust signals. In some cases, attaching an older, authoritative domain to a new one can result in a noticeable boost in traffic and backlink value.
Therefore, a 301 redirect plays a critical role in maintaining SEO integrity, especially during website restructuring or content migration. It ensures that your website remains visible and valuable to both users and search engines despite architectural changes.
Why You Should Not Use a 301 Redirect to the Homepage
Redirecting all old URLs to the homepage or a general site section may seem like a simple solution after a major redesign or migration. However, this approach can cause serious SEO and user experience issues.
Problems of Semantic Relevance
301 redirects should be applied only between pages that are semantically relevant or contain closely related content. Redirecting an old URL to the homepage usually breaks this relevance, as the old and new pages differ in topic and intent. This can lead to the following problems:
Possible Consequences of a 301 Redirect to the Homepage
-
Ignored redirects by Google: Search engines may detect that the redirect leads to unrelated content (such as the homepage) and ignore it. As a result, the old URLs fail to transfer their SEO value.
-
Reduced link equity transfer: Even if such redirects are processed, the transfer of link value is minimal because the homepage typically lacks topic relevance for all redirected URLs. This can cause substantial SEO losses.
-
Soft 404 errors: Google may interpret mass redirects to the homepage as soft 404s, meaning the redirected URLs are treated as non-existent. Consequently, they are removed from the index, and all accumulated authority is lost.
From a user experience standpoint, redirecting visitors to the homepage instead of the expected content often leads to confusion and frustration, increasing bounce rates and reducing engagement.
To prevent these issues, use 301 redirects only to relevant pages with similar content. This approach preserves both user value and SEO performance.
Best Practices for Managing 404 Errors and 301 Redirects
Excessive use of 301 redirects can confuse search engines and negatively impact your rankings.
| Situation / Task | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| 404 | |
| Removing outdated content | Use a 404 error to inform search engines that the content is no longer relevant. |
| Discontinued products | Use a 404 response if no similar product is available as a replacement. |
| Reducing unexpected 404 errors | Regularly scan your website for broken links and fix them promptly. |
| 301 | |
| Preserving user experience | Redirect old URLs to equivalent pages with similar content to ensure a smooth user journey. |
| Optimizing indexing | Maintain accurate redirect maps to facilitate efficient search engine reindexing. |
| Reducing server load | Proper redirect management helps lower the number of 404 responses and improve site performance. |
| Preserving link equity | |
| Using 301 Redirects | Always use 301 redirects when relocating content to transfer up to 90–99% of link value. |
| Avoiding homepage redirects | Redirect to relevant pages instead of the homepage to prevent soft 404s and link equity loss. |
| Monitoring and updating redirects | Regularly audit and update redirect rules to maintain functionality and effectiveness. |
Related Video
404 errors are a normal and expected part of content management on any website. They signal to search engines that certain pages no longer exist, helping maintain the freshness and accuracy of the index. Use 404 responses appropriately — for example, when removing outdated pages or products that are no longer available — to preserve content quality and relevance.
Proper implementation of 301 redirects is crucial for retaining SEO value and ensuring a positive user experience. Redirect old URLs to new, thematically similar pages to maintain most of the original link equity. Avoid mass redirects to the homepage, as this can result in ranking loss and deindexation.
If you require assistance with implementing 301 redirects or optimizing your site structure, consider consulting an SEO specialist. Proper management of redirects and 404 responses ensures that your website remains efficient, relevant, and valuable to both users and search engines.